I am writing this quick tutorial in the hopes it helps someone else out there. There are a few guides out there to do similar tasks to this. They just are not quite what I wanted.
To give everyone an idea on the desired outcome, this is what I wanted to achieve:
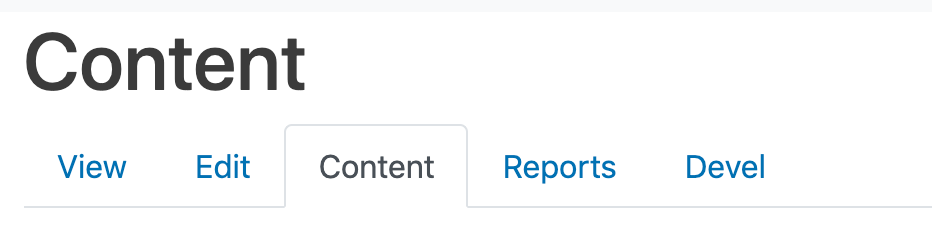
Before I dive into this, I will mention that you can do this with views, if all that you want to produce is content supplied by views. Ivan wrote a nice article on this. In my situation, I wanted a completely custom route, controller and theme function. I wanted full control over the output.
Steps to add sub tabs
Step 1 - create a new module
If you don't already have a module to house this code, you will need one. These commands make use of Drupal console, so ensure you have this installed first.
drupal generate:module --module='Example module' --machine-name='example' --module-path='modules/custom' --description='My example module' --package='Custom' --core='8.x'Step 2 - create a new controller
Now that you have a base module, you need a route
drupal generate:controller --module='example' --class='ExampleController' --routes='"title":"Content", "name":"example.user.contentlist", "method":"contentListUser", "path":"/user/{user}/content"'Step 3 - alter your routes
In order to use magic autoloading, and also proper access control, you can alter your routes to look like this. This is covered in the official documentation.
# Content user tab.
example.user.contentlist:
path: '/user/{user}/content'
defaults:
_controller: '\Drupal\example\Controller\ExampleController::contentListUser'
_title: 'Content'
requirements:
_permission: 'access content'
_entity_access: 'user.view'
user: \d+
options:
parameters:
user:
type: entity:user
# Reports user tab.
example.user.reportList:
path: '/user/{user}/reports'
defaults:
_controller: '\Drupal\example\Controller\ExampleController::reportListUser'
_title: 'Reports'
requirements:
_permission: 'access content'
_entity_access: 'user.view'
user: \d+
options:
parameters:
user:
type: entity:userStep 4 - create example.links.task.yml
This is the code that actually creates the tabs in the user profile. No Drupal console command for this unfortunately. The key part of this is defining base_route: entity.user.canonical.
example.user.content_task:
title: 'Content'
route_name: example.user.contentlist
base_route: entity.user.canonical
weight: 1
example.user.reports_task:
title: 'Reports'
route_name: example.user.reportList
base_route: entity.user.canonical
weight: 2Step 5 - enable the module
Don't forget to actually turn on your custom module, nothing will work until then.
drush en exampleExample module
The best (and simplest) example module I could find that demonstrates this is the Tracker module in Drupal core. The Tracker module adds a tab to the user profile.
